Pci Express Root Complex Drivers
Introduction
The PCI Express (PCIe) module is a multi-lane I/O interconnect providinglow pin count, high reliability, and high-speed data transfer at ratesof up to 8.0 Gbps per lane per direction. It is a 3rd Generation I/O Interconnecttechnology succeeding ISA and PCI bus that is designed to be used as ageneral-purpose serial I/O interconnect in multiple market segments,including desktop, mobile, server, storage and embedded communications.
PCIe Root Complex¶. The PCI Express (PCIe) module is a multi-lane I/O interconnect providing low pin count, high reliability, and high-speed data transfer at rates of up to 8.0 Gbps per lane per direction. Lattice’s PCI Express Root Complex (RC) Lite core provides an x1 or x4 root complex solution from the electrical SERDES interface, physical layer, data link layer and a minimum transaction layer in PCI express protocol stack. This IP is a lighter version of the root complex intended to use in simple bridging application to local bus.
Keystone PCIe
Keystone PCIe module is used on K2H/K2K, K2E, K2L and K2G SoCs. For moredetails on the module specification, please refers to sprugs6d.pdfdocumentation provided at ti.com. The K2G PCIe module spec is part ofspruhy8d.pdf.
Supported platforms
SoCs: K2E, K2G
Keystone PCIe driver may be used on K2L/K2HK and boards/EVMs using theseSoCs, but is not validated since nothing is hooked to PCIe port on theseEVMs.
K2E EVM has a Marvel SATA controller (88se9182) hooked to PCIe port 1.The Driver is validated by connecting a SATA hard disk to the SATA portavailable on the EVM. K2G EVM has a single x1 PCIe slot which acceptsstandard PCIe cards. Following PCIe cards are validated for basicfunctionality on K2G EVM:-
K2G EVM: Make sure following jumper settings on the EVM:-
- PCI Express Root Complex-Standard SATA AHCI Controller-Motherboard resources-HID-compliant vendor-defined device-Intel(R) 8 Series/C220 Series PCI Express Root Port #8 - 8C1E-Intel(R) 8 Series/C220 Series PCI Express Root Port #4 - 8C16-Intel(R) 8 Series/C220 Series PCI Express Root Port #1 - 8C10-Intel(R) Z87 LPC Controller - 8C44 Thank-you!
- Jul 04, 2017 -PCI Express Root Complex-Standard SATA AHCI Controller-Motherboard resources-HID-compliant vendor-defined device-Intel(R) 8 Series/C220 Series PCI Express Root Port #8 - 8C1E-Intel(R) 8 Series/C220 Series PCI Express Root Port #4 - 8C16-Intel(R) 8 Series/C220 Series PCI Express Root Port #1 - 8C10-Intel(R) Z87 LPC Controller - 8C44 Thank-you!
- Chipset driver software for PCI Express Root Port device 9d14 With apologies if I'm in the wrong place for this question; a more obvious forum did not appear.
Introduction to PCIe on TI Keystone platforms
The TI Keystone platforms contain a PCI Express module which supports amulti-lane I/O interconnect providing low pin count, high reliability,and high-speed data transfer at rates of up to 5.0 Gbps per lane perdirection, The module supports Root Complex and End Point operationmodes.
The PCIe driver implemented supports only the Root Complex (RC)operation mode on K2 platforms (K2HK, K2E). The PCIe driver is designedbased on PCIE Designware Core driver. The Designware Core driver isenhanced to support Keystone PCIe driver in the mainline kernel. Thediagram below shows the various drivers that Keystone PCI depends on toimplement the RC driver. PCI Designware Core driver provides a set offunction calls defined in drivers/pci/host/pcie-designware.h forplatform drivers to implement the RC driver. Keystone PCI modulerequired some enhancements to designware core because of the applicationregister space which otherwise is part of the designware core. Thesekeystone specific handling of the driver is re-factored into PCIKeystone DW Core Driver and used from PCI Keystone platform driver. Thisincludes MSI/Legacy IRQ handling, Read/Write functions to write over thePCI bus etc which are unique for Keystone PCI driver.
Connect HDD to an external power supply. Connect the HDD SATA port toK2E EVM SATA port using a 6Gbps data cable and power on the HDD. PowerOn K2E EVM. The K2E rev 1.0.2.0 requires a hardware modification to getthe SATA detection on the PCI bus. Please check with EVM hardware vendorfor the details.
For K2G EVM, there is a PCIe slot available to work with standard PCIecards. For example to test PCIe SATA as in K2E, connect the hard diskSATA cables to the PCIe SATA controller card and insert the card intothe PCIe slot and Power on the EVM. Other PCIe cards can be tested in asimilar way.
Driver Configuration
Assume, you have default configuration set for kernel build. To enablePCI Keystone driver, traverse the following config tree from menuconfig
The RC driver can be built into the kernel as a static module.
Device Tree bindings
DT documentation is atDocumentation/devicetree/bindings/pci/pci-keystone.txt in the kernelsource tree. The PCIE SerDes Phy related DT documentation is availableat Documentation/devicetree/bindings/phy/ti-phy.txt
Driver Source location
The driver code is located at drivers/pci/host
PCI driver calls into Phy SerDes driver to initialize PCI Phy (SerDes).From PCI probe function, phy_init() is called which results in SerDesinitialization. The SerDes code is a common driver used across all subsystems such as SGMII, PCIe and 10G. The driver code for this located atdrivers/phy/phy-keystone-serdes.c
Limitations
- PCIe is verified only on K2E and K2G EVMs
- AER error interrupt is not handled by PCIE AER driver for Keystone asthis uses non standard platform interrupt
- ASPM interrupt is non standard on Keystone and the same is nothandled by the PCIe ASPM driver.
U-Boot environment/scripts
The Keystone PCIe SerDes Phy hardware requires a firmware to configurethe Phy to work as a PCIe phy. As Keystone PCIe is statically built intothe kernel, this firmware is needed when Phy SerDes driver is probed.When initramfs is used as the final rootfs, this firmware can reside at/lib/firmware folder of the fs. For other boot modes (mmc, ubi, nfs),k2-fw-initrd.cpio.gz has this firmware and can be loaded to memory andthe address is passed to kernel through second argument of bootmcommand. Following env scripts are used to customize the u-bootenvironment for various boot modes so that firmware is available toinitialize the phy SerDes when Phy SerDes driver is probed.
firmware file ks2_pcie_serdes.bin is available inti-linux-firmware.git at ti-keystone folder or at /lib/firmware folderof the file system images shipped with the release or under /lib/firmarefolder of the k2-fw-initrd.cpio.gz shipped with the release). If you areusing your own file system, make sure ks2_pcie_serdes.bin resides at/lib/firmware folder.
Setup u-boot env as follows. These are expected to be available in thedefault env variable, but check and update it if not present.

Pci Express Root Complex Driver Download
Add init_fw_rd_${boot} to bootcmd.
Procedure to boot Linux with FS on hard disk
Enable AHCI, ATA drivers
Assume, you have default configuration set for kernel build. Both AHCIand ATA drivers are to be enabled to build statically into the kernelimage if rootfs is mounted from the hard disk. Otherwise, if hard diskis used as a storage device, the below drivers can be built as dynamicmodules and loaded from user space.
From Kernel menuconfig, traverse the configuration tree as follows:-
Boot Linux kernel on K2E EVM using NFS file system or Ramfs and usingrootfs provided in the SDK. Make sure SATA HDD is connected to EVM asexplained above and SATA EP is detected during boot up. This exampleuses a 1TB HDD and create two partition. First partition is forfilesystem and is 510GB and second is for swap and is 256MB.
Create partition with fdisk
First step is to create 2 partitions using fdisk command. At Linuxconsole type the following commands
Format partitions
Pci Express Root Complex Drivers Free
Copy filesystem to rootfs
This procedure assumes the cpio file for SDK filesystem is available onthe NFS or ramfs.
Where rootfs.cpio is the cpio file for the SDK fileystem.
Booting with FS on harddisk
Once the harddisk is formatted and has a rootfs installed, followingprocedure can be used to boot Linux kernel using this rootfs.
Boot EVM to u-boot prompt. Add following env variables to u-bootenvironment :-
Now type boot command and boot to Linux. The above steps can be skippedonce u-boot implements these env variables by default which is expectedto be supported in the future.
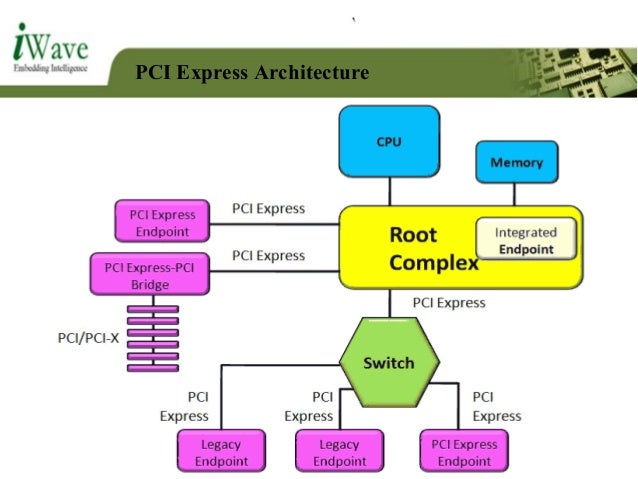
RC Software Architecture
Following is the software architecture for Root Complex mode:
Following is a brief explanation of layers shown in the diagram:
Pci Express Root Complex Driver Windows 10 Update
- There are different drivers for the connected PCIe devices likepci_endpoint_test, tg-3, r8169, xhci-pci, ahci, etc. It could bevendor-specific like most of the ethernet cards (tg3, r8169) or class-specificlike xhci-pci and ahci. Each of these drivers will also interact with it’s owndomain-specific stack. For example, tg3 will interface with network stack, andxhci-pci will interface with USB stack.
- The PCI core layer scans the PCIe bus to identify and detect any PCIe devices.It also binds the driver from the layer above, for the PCIe device, based onvendorid, deviceid and class.
- The PCI BIOS layer handles resource management. For example, allocation ofmemory resources for BARs.
- The bottom-most layer consists of the PCIe platform drivers like pcie-cadence,pcie-designware, etc. pci-j721e and pci-dra7xx are TI’s wrappers over thesedrivers. They configure platform-specific controllers and performactual register writes.
Overview of the Pci technology.
The Pci technology is not associated with any headers.
Enumerations
| Title | Description |
|---|---|
| NPEM_CONTROL_STANDARD_CONTROL_BIT |
Functions
| Title | Description |
|---|---|
| ENABLE_VIRTUALIZATION | The EnableVirtualization routine enables or disables virtualization for a PCI Express (PCIe) device that supports the single root I/O virtualization (SR-IOV) interface. |
| GET_VIRTUAL_DEVICE_DATA | The GetVirtualFunctionData routine reads data from the PCI Express (PCIe) configuration space of a virtual function (VF) on a device that supports the single root I/O virtualization (SR-IOV) interface. |
| GET_VIRTUAL_DEVICE_LOCATION | The GetLocation routine returns the device location of a PCI Express (PCIe) virtual function (VF) on a PCI bus. A device that supports the single root I/O virtualization (SR-IOV) interface can expose one or more VFs on the PCI bus. |
| GET_VIRTUAL_DEVICE_RESOURCES | The GetResources routine returns the resources that the PCI Express (PCIe) physical function (PF) requires in order to enable virtualization on a device that supports the single root I/O virtualization (SR-IOV) interface. |
| GET_VIRTUAL_FUNCTION_PROBED_BARS | The GetVirtualFunctionProbedBars routine returns the values of the PCI Express (PCIe) Base Address Registers (BARs) of a device that supports the single root I/O virtualization (SR-IOV) interface. |
| NPEM_CONTROL_ENABLE_DISABLE | |
| NPEM_CONTROL_QUERY_STANDARD_CAPABILITIES | |
| NPEM_CONTROL_SET_STANDARD_CONTROL | |
| SET_VIRTUAL_DEVICE_DATA | The SetVirtualFunctionData routine writes data to the PCI Express (PCIe) configuration space of a virtual function (VF) on a device that supports the single root I/O virtualization (SR-IOV) interface. |
Pci Express Root Complex Drivers Download
Structures
Pci Express Root Complex Definition
| Title | Description |
|---|---|
| NPEM_CAPABILITY_STANDARD | |
| NPEM_CONTROL_INTERFACE | |
| PCI_CAPABILITIES_HEADER | The PCI_CAPABILITIES_HEADER structure defines a header that is present in every PCI capability structure. |
| PCI_DEVICE_PRESENT_INTERFACE | The PCI_DEVICE_PRESENT_INTERFACE structure is reserved for system use. |
| PCI_EXPRESS_AER_CAPABILITIES | The PCI_EXPRESS_AER_CAPABILITIES structure describes a PCI Express (PCIe) advanced error capabilities and control register of a PCIe advanced error reporting capability structure. |
| PCI_EXPRESS_AER_CAPABILITY | The PCI_EXPRESS_AER_CAPABILITY structure describes a PCI Express (PCIe) advanced error reporting capability structure. |
| PCI_EXPRESS_BRIDGE_AER_CAPABILITY | The PCI_EXPRESS_BRIDGE_AER_CAPABILITY structure describes a PCI Express (PCIe) advanced error reporting capability structure for a PCIe bridge device. |
| PCI_EXPRESS_CAPABILITIES_REGISTER | The PCI_EXPRESS_CAPABILITIES_REGISTER structure describes a PCI Express (PCIe) capabilities register of a PCIe capability structure. |
| PCI_EXPRESS_CAPABILITY | The PCI_EXPRESS_CAPABILITY structure describes a PCI Express (PCIe) capability structure. |
| PCI_EXPRESS_CORRECTABLE_ERROR_MASK | The PCI_EXPRESS_CORRECTABLE_ERROR_MASK structure describes a PCI Express (PCIe) correctable error mask register of a PCIe advanced error reporting capability structure. |
| PCI_EXPRESS_CORRECTABLE_ERROR_STATUS | The PCI_EXPRESS_CORRECTABLE_ERROR_STATUS structure describes a PCI Express (PCIe) correctable error status register of a PCIe advanced error reporting capability structure. |
| PCI_EXPRESS_DESIGNATED_VENDOR_SPECIFIC_CAPABILITY | Represents the Designated Vendor-Specific Extended Capability defined by PCI-SIG. |
| PCI_EXPRESS_DESIGNATED_VENDOR_SPECIFIC_HEADER_1 | Represents the Designated Vendor-Specific Extended Capability Header 1 defined by PCI-SIG. |
| PCI_EXPRESS_DESIGNATED_VENDOR_SPECIFIC_HEADER_2 | Represents the Designated Vendor-Specific Extended Capability Header 2 defined by PCI-SIG. |
| PCI_EXPRESS_DEVICE_CAPABILITIES_REGISTER | The PCI_EXPRESS_DEVICE_CAPABILITIES_REGISTER structure describes a PCI Express (PCIe) device capabilities register of a PCIe capability structure. |
| PCI_EXPRESS_DEVICE_CONTROL_REGISTER | The PCI_EXPRESS_DEVICE_CONTROL_REGISTER structure describes a PCI Express (PCIe) device control register of a PCIe capability structure. |
| PCI_EXPRESS_DEVICE_STATUS_REGISTER | The PCI_EXPRESS_DEVICE_STATUS_REGISTER structure describes a PCI Express (PCIe) device status register of a PCIe capability structure. |
| PCI_EXPRESS_DPC_CAPABILITY | |
| PCI_EXPRESS_DPC_CAPS_REGISTER | |
| PCI_EXPRESS_DPC_CONTROL_REGISTER | |
| PCI_EXPRESS_DPC_RP_PIO_EXCEPTION_REGISTER | |
| PCI_EXPRESS_DPC_RP_PIO_HEADERLOG_REGISTER | |
| PCI_EXPRESS_DPC_RP_PIO_IMPSPECLOG_REGISTER | |
| PCI_EXPRESS_DPC_RP_PIO_MASK_REGISTER | |
| PCI_EXPRESS_DPC_RP_PIO_SEVERITY_REGISTER | |
| PCI_EXPRESS_DPC_RP_PIO_STATUS_REGISTER | |
| PCI_EXPRESS_DPC_RP_PIO_SYSERR_REGISTER | |
| PCI_EXPRESS_DPC_RP_PIO_TLPPREFIXLOG_REGISTER | |
| PCI_EXPRESS_DPC_STATUS_REGISTER | |
| PCI_EXPRESS_ENHANCED_CAPABILITY_HEADER | The PCI_EXPRESS_ENHANCED_CAPABILITY_HEADER structure describes the header for a PCI Express (PCIe) extended capability structure. |
| PCI_EXPRESS_ERROR_SOURCE_ID | The PCI_EXPRESS_ERROR_SOURCE_ID structure describes the identifiers of the first correctable error and the first uncorrectable error that are reported in the PCI Express (PCIe) root error status register. |
| PCI_EXPRESS_LANE_ERROR_STATUS | |
| PCI_EXPRESS_LINK_CAPABILITIES_REGISTER | The PCI_EXPRESS_LINK_CAPABILITIES_REGISTER structure describes a PCI Express (PCIe) link capabilities register of a PCIe capability structure. |
| PCI_EXPRESS_LINK_CONTROL_REGISTER | The PCI_EXPRESS_LINK_CONTROL_REGISTER structure describes a PCI Express (PCIe) link control register of a PCIe capability structure. |
| PCI_EXPRESS_LINK_CONTROL3 | |
| PCI_EXPRESS_LINK_QUIESCENT_INTERFACE | The PCI_EXPRESS_LINK_QUIESCENT_INTERFACE structure is reserved for system use. |
| PCI_EXPRESS_LINK_STATUS_REGISTER | The PCI_EXPRESS_LINK_STATUS_REGISTER structure describes a PCI Express (PCIe) link status register of a PCIe capability structure. |
| PCI_EXPRESS_NPEM_CAPABILITY | |
| PCI_EXPRESS_NPEM_CAPABILITY_REGISTER | |
| PCI_EXPRESS_NPEM_CONTROL_REGISTER | |
| PCI_EXPRESS_NPEM_STATUS_REGISTER | |
| PCI_EXPRESS_PME_REQUESTOR_ID | The PCI_EXPRESS_PME_REQUESTOR_ID structure describes the identifier of the requester of a power management event (PME). |
| PCI_EXPRESS_PTM_CAPABILITY | Reserved. Do not use. |
| PCI_EXPRESS_PTM_CAPABILITY_REGISTER | Reserved. Do not use. |
| PCI_EXPRESS_PTM_CONTROL_REGISTER | Reserved. Do not use. |
| PCI_EXPRESS_ROOT_CAPABILITIES_REGISTER | The PCI_EXPRESS_ROOT_CAPABILITIES_REGISTER structure describes a PCI Express (PCIe) root capabilities register of a PCIe capability structure. |
| PCI_EXPRESS_ROOT_CONTROL_REGISTER | The PCI_EXPRESS_ROOT_CONTROL_REGISTER structure describes a PCI Express (PCIe) root control register of a PCIe capability structure. |
| PCI_EXPRESS_ROOT_ERROR_COMMAND | The PCI_EXPRESS_ROOT_ERROR_COMMAND structure describes a PCI Express (PCIe) root error command register of a PCIe advanced error reporting capability structure. |
| PCI_EXPRESS_ROOT_ERROR_STATUS | The PCI_EXPRESS_ROOT_ERROR_STATUS structure describes a PCI Express (PCIe) root error status register of a PCIe advanced error reporting capability structure. |
| PCI_EXPRESS_ROOT_PORT_INTERFACE | The PCI_EXPRESS_ROOT_PORT_INTERFACE structure is reserved for system use. |
| PCI_EXPRESS_ROOT_STATUS_REGISTER | The PCI_EXPRESS_ROOT_STATUS_REGISTER structure describes a PCI Express (PCIe) root status register of a PCIe capability structure. |
| PCI_EXPRESS_ROOTPORT_AER_CAPABILITY | The PCI_EXPRESS_ROOTPORT_AER_CAPABILITY structure describes a PCI Express (PCIe) advanced error reporting capability structure for a root port or a root complex event collector. |
| PCI_EXPRESS_SEC_AER_CAPABILITIES | The PCI_EXPRESS_SEC_AER_CAPABILITIES structure describes a PCI Express (PCIe) secondary error capabilities and control register of a PCIe advanced error reporting capability structure. |
| PCI_EXPRESS_SEC_UNCORRECTABLE_ERROR_MASK | The PCI_EXPRESS_SEC_UNCORRECTABLE_ERROR_MASK structure describes a PCI Express (PCIe) secondary uncorrectable error mask register of a PCIe advanced error reporting capability structure. |
| PCI_EXPRESS_SEC_UNCORRECTABLE_ERROR_SEVERITY | The PCI_EXPRESS_SEC_UNCORRECTABLE_ERROR_SEVERITY structure describes a PCI Express (PCIe) secondary uncorrectable error severity register of a PCIe advanced error reporting capability structure. |
| PCI_EXPRESS_SEC_UNCORRECTABLE_ERROR_STATUS | The PCI_EXPRESS_SEC_UNCORRECTABLE_ERROR_STATUS structure describes a PCI Express (PCIe) secondary uncorrectable error status register of a PCIe advanced error reporting capability structure. |
| PCI_EXPRESS_SECONDARY_CAPABILITY | |
| PCI_EXPRESS_SERIAL_NUMBER_CAPABILITY | The PCI_EXPRESS_SERIAL_NUMBER_CAPABILITY structure describes a serial number for a PCI Express (PCIe) device. |
| PCI_EXPRESS_SLOT_CAPABILITIES_REGISTER | The PCI_EXPRESS_SLOT_CAPABILITIES_REGISTER structure describes a PCI Express (PCIe) slot capabilities register of a PCIe capability structure. |
| PCI_EXPRESS_SLOT_CONTROL_REGISTER | The PCI_EXPRESS_SLOT_CONTROL_REGISTER structure describes a PCI Express (PCIe) slot control register of a PCIe capability structure. |
| PCI_EXPRESS_SLOT_STATUS_REGISTER | The PCI_EXPRESS_SLOT_STATUS_REGISTER structure describes a PCI Express (PCIe) slot status register of a PCIe capability structure. |
| PCI_EXPRESS_UNCORRECTABLE_ERROR_MASK | The PCI_EXPRESS_UNCORRECTABLE_ERROR_MASK structure describes a PCI Express (PCIe) uncorrectable error mask register of a PCIe advanced error reporting capability structure. |
| PCI_EXPRESS_UNCORRECTABLE_ERROR_SEVERITY | The PCI_EXPRESS_UNCORRECTABLE_ERROR_SEVERITY structure describes a PCI Express (PCIe) uncorrectable error severity register of a PCIe advanced error reporting capability structure. |
| PCI_EXPRESS_UNCORRECTABLE_ERROR_STATUS | The PCI_EXPRESS_UNCORRECTABLE_ERROR_STATUS structure describes a PCI Express (PCIe) uncorrectable error status register of a PCIe advanced error reporting capability structure. |
| PCI_FPB_CAPABILITIES_REGISTER | The Flattening Portal Bridge (FPB) Capabilities register. See section 7.y.2. |
| PCI_FPB_CAPABILITY | Flattening Portal Bridge (FPB) Capabilities that is required for any bridge Function that implements FPB. See section 7.y. |
| PCI_FPB_CAPABILITY_HEADER | The Flattening Portal Bridge (FPB) Capabilities header. See section 7.y.1. |
| PCI_FPB_MEM_HIGH_VECTOR_CONTROL1_REGISTER | The FPB MEM High Vector Control 1 Register. See section 7.y.6. |
| PCI_FPB_MEM_HIGH_VECTOR_CONTROL2_REGISTER | The FPB MEM High Vector Control 2 Register. See section 7.y.7. |
| PCI_FPB_MEM_LOW_VECTOR_CONTROL_REGISTER | FPB MEM Low Vector Control Register. See section 7.y.5. |
| PCI_FPB_RID_VECTOR_CONTROL1_REGISTER | The FPB RID Vector Control 1 Register. See section 7.y.3. |
| PCI_FPB_RID_VECTOR_CONTROL2_REGISTER | The FPB RID Vector Control 1 Register. See section 7.y.3. |
| PCI_FPB_VECTOR_ACCESS_CONTROL_REGISTER | The FPB Vector Access Control Register. See section 7.y.8. |
| PCI_FPB_VECTOR_ACCESS_DATA_REGISTER | The FPB Vector Access Data Register. See section 7.y.9. |
| PCI_PM_CAPABILITY | The PCI_PM_CAPABILITY structure reports the power management capabilities of the device. |
| PCI_PMC | The PCI_PMC structure is used to report the contents of the power management capabilities register. |
| PCI_PMCSR | The PCI_PMCSR structure is used to report the contents of the device's power management control status register. |
| PCI_PMCSR_BSE | The PCI_PMCSR_BSE structure is used to report the contents of the power management control status register for PCI bridge support extensions. |
| PCI_X_CAPABILITY | The PCI_X_CAPABILITY structure reports the contents of the command and status registers of a device that is compliant with the PCI-X Addendum to the PCI Local Bus Specification. |